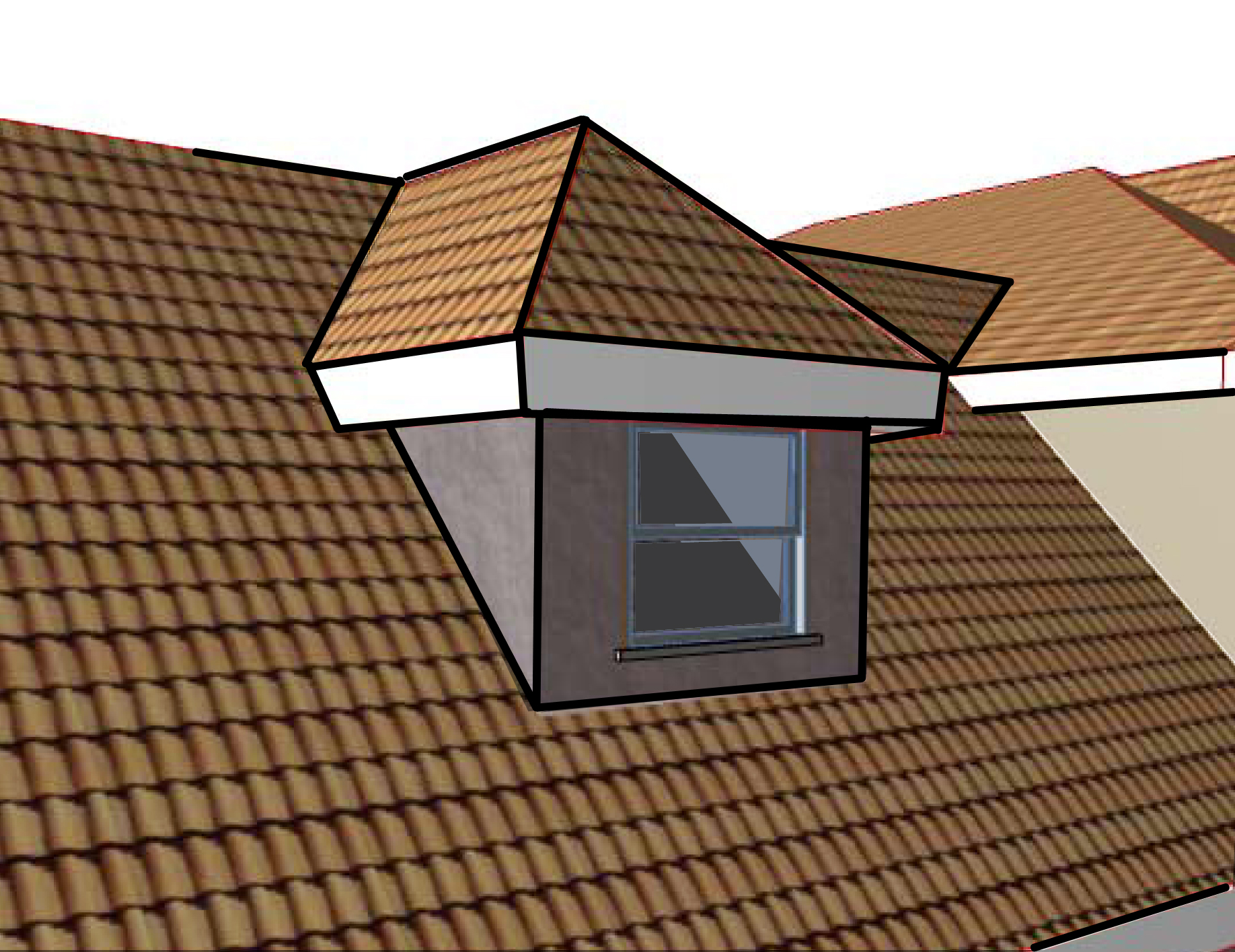
Dormers are architectural elements that project from a sloping roof, adding both functional and aesthetic value to buildings. These structures are typically used to increase the usable space in attics and upper floors, providing additional headroom, natural light, and ventilation. Dormers can be designed in various styles, including gabled, hipped, shed, and eyebrow, each contributing differently to the building’s appearance. Their versatility and practical benefits make dormers a popular choice in residential architecture, offering a blend of elegance and utility.
Types of Buildings with Dormers
Dormers are commonly found in a variety of building types, from traditional homes to modern constructions. They are particularly prevalent in older, historic houses, where they add charm and character, as well as in contemporary designs that aim to maximize space and light. Dormers are also a common feature in cottage-style homes, bungalows, and Cape Cod houses. Their presence can significantly enhance the curb appeal of a property, making them a desirable addition for homeowners and builders alike.
Materials Used for Dormers
When it comes to materials, dormers can be constructed using a range of options to match or complement the existing roof and exterior of the building. Common materials include wood, vinyl, aluminum, and fiber cement. Wooden dormers offer a classic, timeless look but require regular maintenance to prevent rot and decay. Vinyl and aluminum are low-maintenance alternatives that provide durability and weather resistance. Fiber cement combines the aesthetic appeal of wood with the durability of synthetic materials, making it a popular choice for modern dormer construction.
Potential Issues with Dormers
Despite their many advantages, dormers can present certain challenges, particularly related to weatherproofing. One common issue is the potential for leaks, especially around the dormer windows and where the dormer meets the main roof. Proper flashing and sealing are crucial to prevent water infiltration. Additionally, dormers can contribute to ice damming, where melting snow refreezes at the eaves, leading to water backup and potential roof damage. Ensuring adequate insulation and ventilation in the attic can help mitigate this problem.
Conclusion
In conclusion, dormers are a versatile and valuable addition to many types of buildings, enhancing both space and aesthetic appeal. They can be constructed from various materials to suit different architectural styles and preferences. However, it is essential to address potential issues such as leaks and ice damming through careful design and maintenance. By doing so, homeowners can enjoy the benefits of dormers without compromising the integrity of their roofs. Whether for added space, light, or simply to boost curb appeal, dormers continue to be a popular and practical architectural feature.